Services
Omega-3 Index Testing
Are you at risk for cardiovascular disease, chronic inflammation, or struggling with mental health, cognition, vision, skin health, or low energy levels? These concerns are often influenced by omega-3 fatty acid status—yet many people don’t know where they stand. Checking your Omega-3 Index provides valuable insight into whether your body is getting the essential fats it needs to support cellular health, reduce inflammation, and promote long-term wellness.
What Is the Omega-3 Index?
The Omega-3 Index is a simple finger-stick blood test that quantifies the levels of two essential omega-3 fatty acids—EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid)—in your red blood cells.
Unlike short-term dietary assessments, this test measures how much EPA and DHA are incorporated into red blood cell membranes, providing a reliable reflection of your long-term omega-3 status over the past several months.
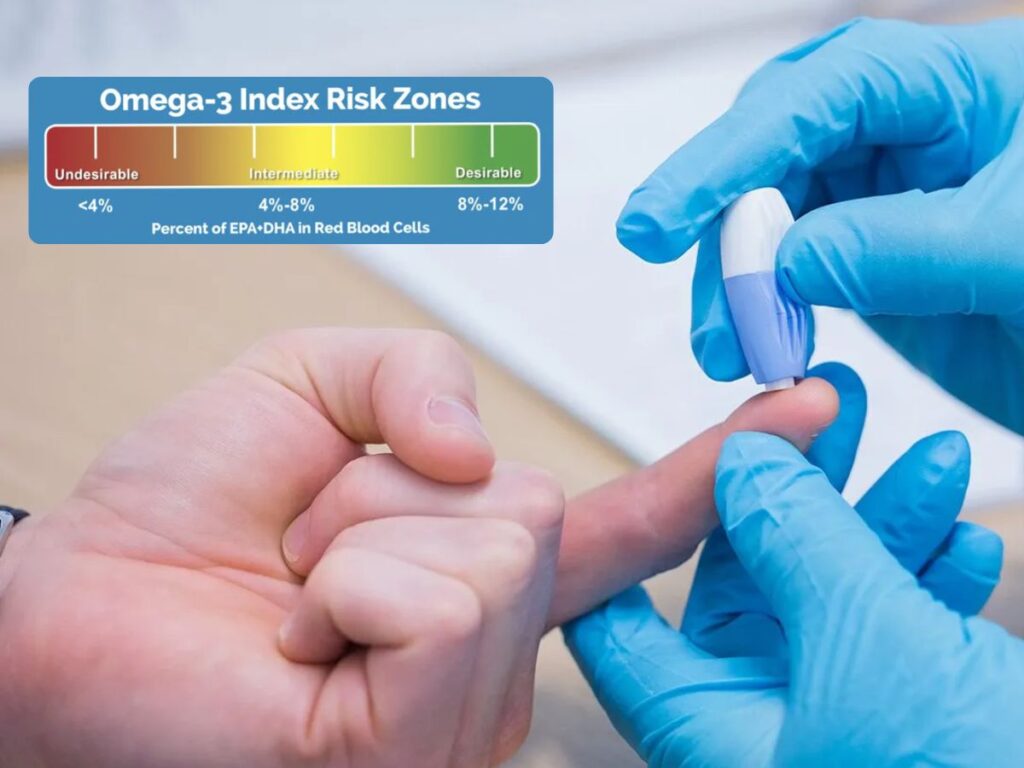
Understanding Your Omega-3 Index Score
Your Omega-3 Index result is reported as a percentage, representing the proportion of EPA and DHA within your red blood cell membranes.
- 8% or higher is considered the ideal, lowest-risk zone
- Around 6% or below is where many individuals fall
- 4% or below represents the highest-risk zone
Most people in the U.S. fall at or below 4%, placing them at high risk. Individuals in this range may have up to a 90% higher risk of sudden cardiac death compared to those in the optimal range.
What Does a Low Omega-3 Index Put You at Risk For?
A low Omega-3 Index reflects chronically inadequate levels of EPA and DHA—fats that are critical for cellular integrity, inflammation control, and cardiovascular stability. Over time, this deficiency may increase the risk for a wide range of health concerns.
- Cardiovascular Disease & Sudden Cardiac Death: Low omega-3 levels are strongly associated with increased cardiovascular risk. EPA and DHA help stabilize heart cell membranes, regulate heart rhythm, reduce triglycerides, and support healthy blood vessel function. Individuals in the lowest Omega-3 Index range face significantly higher risks of heart attack, arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death.
- Chronic Inflammation: Omega-3 fatty acids help regulate the body’s inflammatory response. When levels are low, inflammation may remain chronically elevated, contributing to joint pain, autoimmune conditions, metabolic dysfunction, and accelerated aging.
- Brain Health, Cognition & Mental Health: DHA is a primary structural component of the brain and nervous system. Insufficient omega-3 levels have been linked to brain fog, memory challenges, mood imbalance, anxiety, and depression, and may impair long-term cognitive resilience.
- Vision & Eye Health: DHA is highly concentrated in the retina. Low omega-3 levels may contribute to dry eyes, visual strain, and age-related vision changes, particularly in individuals with heavy screen exposure.
- Skin Health & Cellular Barrier Function: Omega-3s support skin hydration and barrier integrity. Deficiency may present as dry skin, eczema, increased sensitivity, and slower healing—often reflecting broader membrane dysfunction throughout the body.
- Low Energy, Poor Recovery & Stress Tolerance: Because omega-3s influence mitochondrial function and cellular signaling, low levels may contribute to fatigue, impaired recovery, reduced stress resilience, and diminished overall vitality.
The Cardioprotective Demographic
Individuals with optimal Omega-3 Index levels—often referred to as the cardioprotective demographic—typically achieve these ranges by consuming three servings of high-quality fatty fish per week, combined with daily supplementation using a high-quality omega-3.
If you’re not already consuming high qualities of fatty, non-fried fish, and/or not supplementing high quality Omega 3 oil, and/or you’re concerned about your risk status, book an appointment to get your Omega 3 index tested today!
